Science tourism
Definitions of Tourism and Objectives of the Tourism Development

Definition of the Tourism
The Definition of Tourism varies source by source, person by person. There is no consensus concerning the definition of tourism and each and every institution define "Tourism" differently.
- Definition of the Tourism by UNWTO:
"Tourism comprises the activities of persons traveling to and staying in places outside their usual environment for not more than one consecutive year for leisure, business and other purposes".
- Nature and Classification of Tourism:
Tourism is characterized as a phenomenon that is highly influenced by factors such as seasonality, change in income, change in taste and lifestyle, and attitude. Tourism can be differentiated from other travels in terms of purpose and duration of visit and behavior of travelers at destinations. Tourism encompasses travel for pleasure, holiday, health, business, pilgrimage, education, and other motivations without involvement in remunerative activities. The duration of a tour should be at least 24 hours to distinguish between a tourist and an excursionist and it may be extended to a maximum duration of one year.
Definitions of the Tourism and Tourist
Different definitions by different countries:
- U. S. A
The tourist shall be “a person who travels away from home for a distant of at least 50 miles (one way) for business, pleasure, personal affairs, or any other purpose except to commute to work whether he stays overnight or returns the same day”, National Tourism Resources and Review Commission (NTRRC)
- United Kingdom
The tourist trips include all overnight trips away from home by residents for holidays, visits to friends and relatives (non-holiday), business and conference trips and trips for any other purpose. Five types of visitor groups; holiday independent, holiday inclusive, business, VFR and miscellaneous. The National Tourist Board (NTBs) of England, Scotland and Northern Ireland
- Japan
There is no clear definition on the term of Tourism in Japan, but one academia tried to define as “Tourism is the activities of a person who will leave the environment of normal resident with an intension to return again to his normal residence, seeking for different modes of recreation” by Masuzo Inoue.
- Canada
The Canadian Travel Survey (CTS) defined tourism on the lines of US definitions, but relaxing on the distance of 50 miles to 25 miles.
- Australia
The Australian Bureau of Industry (ABI) define on the line of US definition, but fixing the distance at 40 kilometers. They also allowed temporary and recreational visits to second homes as part of tourism but not visits by local residents.
Objectives of the Tourism Development (1)
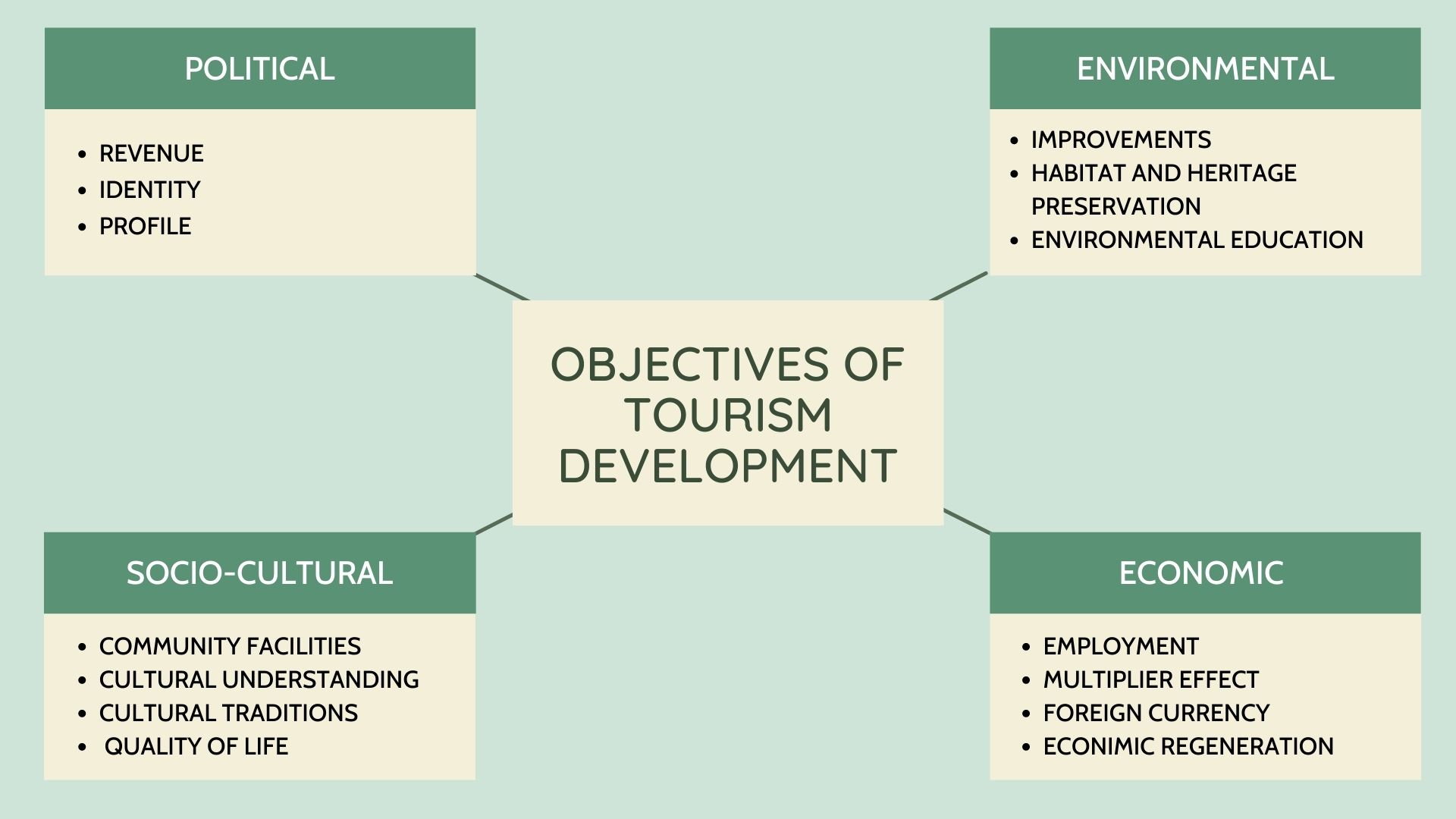
Objectives of the Tourism Development (2)
1. Economic Objectives
Tourism is the world's largest industry and one of the objectives of tourism development is economic gain. In economic terms the travel and tourism industry is able to do three key things: 1) It gives vigor to economies. 2) It offers people jobs and career prospects. 3) It stimulates development.
2. Environmental Objectives
Protection of the environment is essential and the main environmental objective of tourism are; 1) Habitat preservation, 2) Regeneration and conservation of the build and natural environment, 3) Environmental education and 4) Environmental improvements.
3. Socio-cultural Objectives
Tourism brings people of different countries together and we all need to increase our awareness and understanding of different cultures. The main socio-cultural objectives of tourism development are: 1) To promote understanding of different cultures, 2) To improve quality of life for the local population, 3) To provide community facilities, as well as tourist facilities, 4) To develop a sense of pride in traditional culture and identity.
4. Political Objectives
Governments can have a influence on the patterns of travel not only directly but also indirectly through their wider activities, and the political climate that they promote. Investment by governments in the infrastructure has also led to an increase in visitor numbers and visitor spending. Thus political objectives can include: 1) Enhancing the image of an area and 2) Creating a regional or national identity.
Positive and Negative Impacts of Tourism Development
.jpg)
Sustainable Tourism Development
Tourism is often developed at specific locations and concentrates growth in the same area. There may be competition for space and tourism construction, especially hotels, may be inappropriate in scale and style with respect to other structures and the landscape. Congregations of people create congestion and crowding that ultimately produces stress, annoyance, anger and other negative attitudes.
An environmental assessment determines the impact of a proposed action on the environment which includes changes in social, cultural, economic, biological, physical and ecological systems. The meaning of sustainable development was defined in the report of “Our Common Future” by Brundtland Commission in 1987. The declaration on Sustainable Tourism Development (STD) was adopted at the UNWTO forum in 1996 in Bali and in 1997 in Male respectively. Thus, sustainable development is defined as “Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generation to meet their own needs”.
Agenda 21 which was agreed in the United Nations Convention on Education and Development (UNCED) held in 1992 at in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, has laid emphasis on ten priority areas for action by the travel and tourism industry; Waste minimization, Re-use and recycling, Energy efficiency, Conservation and management of freshwater resources, Waste water treatment, Hazardous substances, Planning and management of transport, Land-use planning and management, Involving staff, customers, and community members in environmental issues and Design for sustainability and partnership for sustainability.
Formulation of a sound Tourism Policy
Multiplier Effects of Tourism Development (1)
Multiplier Effects of Tourism Development (2)
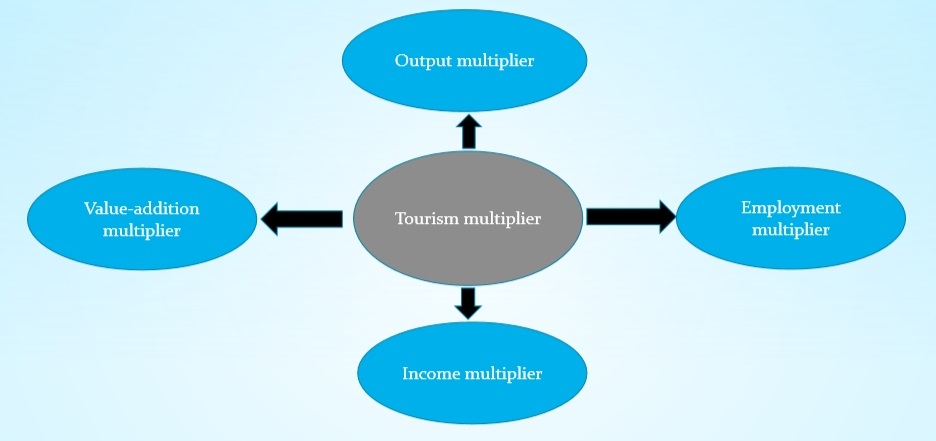
The expenditure of tourists passes through the different sections of the economy. The compound effects of expenditure in the host destination start at front-line tourist establishments such as hotels, restaurants, and transport. The effect of this expenditure seeps into other segments of the host economy at the direct, indirect and induced levels. This is generally known as the multiplier effect. The effect of change in the local economy through tourism development are measured in several ways, depending upon the priority of the results; employment and incomes, total value added to the local economy.
Output and sales multiplier:
Sales multiplier measures the volume and value of sales whereas output multiplier compute changes in the actual level of production. This is the measurement of the amount of additional business revenue generated in the economy.
Employment multiplier:
The employment multiplier measures the total change in employment, resulting from an initial change in employment in an exporting industry. The additional employment in the new activity, multiplied by the employment multiplier for the industry, provides an estimation of the total number of jobs created in the destination region.
Income multiplier:
The income multiplier captures the generation of additional incomes such as wages, salaries, rent, interest and profit due to increased tourist spending.
Value-added multiplier:
The estimation of the value-added multiplier provides a magniture of the addition of value to the existing product as a result of the economic activities such as employee compensation, indirect business, hike in property tax and other property income.
Tourism Marketing Planning (1)
Marketing is a combination of activities to motivate people to buy the product. A marketing programmecombines a number of aspects for an integrated, viable and strategic plan which is known as marketing mix. The marketing mix which consists of Product, Price, Promotion and Price was introduced by E. J. McCarthy in the year of 1960. This 4 Ps have been expanded its meaning and significance by marketing professionals to 8 Ps in order to better position the products strategically in the tourism market.
Definitions and Objectives of the Tourism Marketing
Definition of Marketing by American Marketing Association (AMA)2016: “the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging of offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large”
Science tourism










